Self-Checkout Development in Mobile Apps – Benefits, Implementation Approaches and Technology Stack

Self-checkout is a retail technology where customers scan, bag, and pay for their purchases without assistance from a cashier. So, instead of waiting in traditional checkout lines, customers use self-service kiosks or mobile apps to complete their transactions. These self-checkouts are becoming popular across the UAE as more and more retail chains, grocery stores and dining outlets implement this new convenience for their customers.

How Self-Checkout Works in Mobile Apps
In mobile apps, self-checkout enables customers to use their smartphones to scan items as they shop, add them to a virtual cart, and make payments directly within the app. Some systems use QR codes, barcodes, or RFID technology for item scanning. Once payment is completed, the app generates a digital receipt, and customers can leave the store without standing in line for bill payments.
Traditional Checkout Vs Self-Checkout
| Category | Traditional Checkout | Self-Checkout |
| Cashier Oversight | Cashiers visually monitor transactions to prevent theft | Direct human observation reduces theft risk. |
| Theft Risks | Lower, as cashiers verify scanned items & pricing | Human verification of items and pricing reduces errors and fraud. |
| AI-Based Monitoring | Not applicable | No automated AI-based fraud detection. |
| Weight Verification | Not common | Typically not used for item verification. |
| Random Audits | Cashiers may manually verify high-value purchases | Manual checks of high-value items for fraud prevention. |
| Payment Security | PCI-compliant payment terminals | Standard payment security measures. |
| User Authentication | Not required | No user authentication required. |
| RFID/NFC Technology | Rarely used | Limited use of RFID/NFC technologies. |
| Self-Checkout | ||
| Cashier Oversight | No cashier oversight, increasing risk of theft | Lack of direct human observation increases theft risk. |
| Theft Risks | Higher risk of “skip-scanning” (scanning cheap items…) | Vulnerable to “skip-scanning” and other fraud methods. |
| AI-Based Monitoring | AI-powered fraud detection flags unusual behaviors | Automated fraud detection using AI algorithms. |
| Weight Verification | Some systems use weight sensors to match scanned items | Weight sensors verify scanned items to prevent fraud. |
| Random Audits | Systems can trigger random manual checks for fraud prevention | Automated or triggered random audits for fraud prevention. |
| Payment Security | End-to-end encryption, tokenized payments, and NFC security | Advanced security measures for secure transactions. |
| User Authentication | Some apps use biometric authentication (Face ID, …) | Biometric authentication enhances security. |
| RFID/NFC Technology | Can integrate RFID/NFC for automatic scanning & theft prevention | Potential for automated scanning and theft prevention using RFID/NFC. |
Benefits of Self-Checkout for Retailers
Here are top 7 reasons we recommend businesses go for selfcheckout development:
1. Faster Transactions
Self-checkouts reduce long queues and wait times. Customers at dining points, grocery stores and retail chains skip long queues – which directly improves customer experience.
2. Lower Labor Costs
Because self-checkouts inherently don’t require external assistance, let’s say, from cashiers and representatives, more staff can focus on sensitive areas like inventory and complaint resolution.
3. Increased Sales
Faster checkouts encourage impulse purchases and reduce cart abandonment, while more customers complete transactions without frustration.
4. Space Efficiency
Self-checkout kiosks and mobile-based solutions take up significantly less space than traditional cashier lanes so stores become space-efficient and accommodate more shoppers.
5. Customer Convenience
Shoppers enjoy greater autonomy with quicker transactions, eliminate the need to wait in long lines which is perfect for customers who prefer a hassle-free, self-service experience.
6. Data Collection & Personalization
Mobile self-checkout solutions help retailers track purchasing behavior so they can offer personalized recommendations, targeted promotions, and loyalty rewards in real-time.
7. Theft Prevention with AI & RFID
AI-powered self-checkout systems use computer vision, object detection, weight sensors, and RFID technology to detect un-scanned items or suspicious behavior to minimize shrinkage and theft.
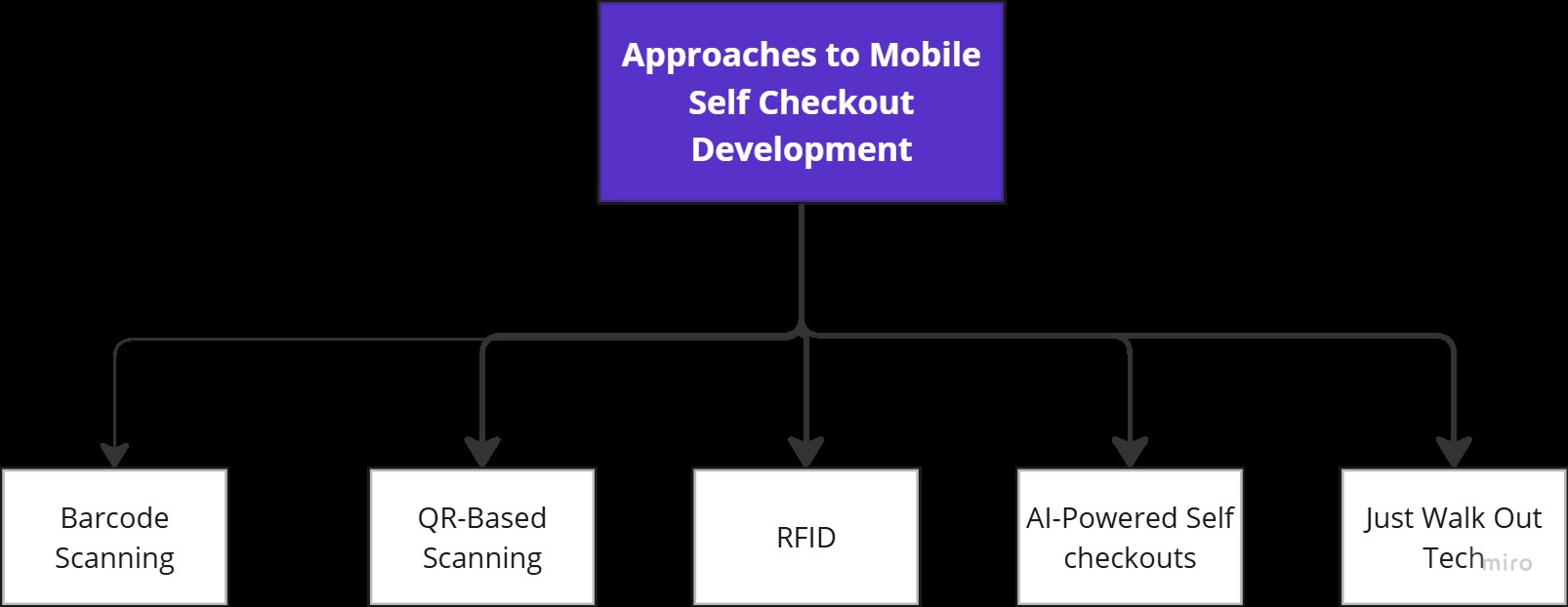
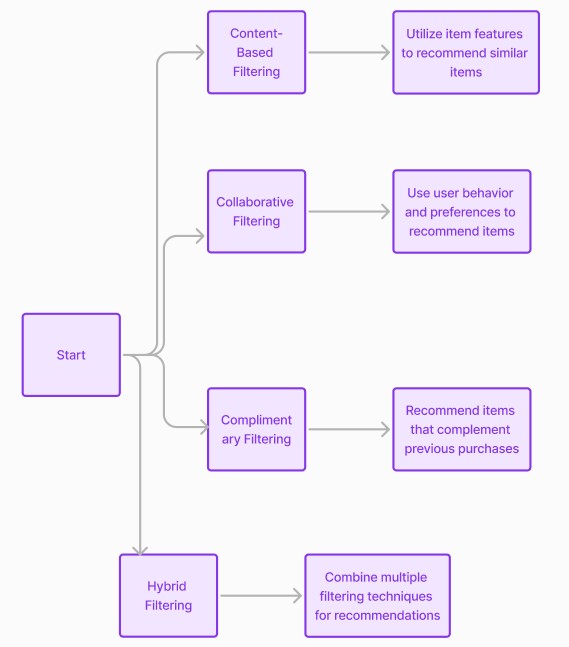
Approaches to Implementing Self-Checkout in Mobile Apps
There are five common approaches to implementing self-checkout systems via mobile applications. These approaches use diverse technologies and are suitable for different store types and customer experience goals.
1. Barcode Scanning-Based Self-Checkout
Barcode scanning is the simplest approach to implement self-checkout. A customer uses the retailer’s mobile application to scan product barcodes during/after shopping. This app adds scanned items to a virtual cart. At checkout, customers pay directly through the app using digital payment methods. Such apps typically generate digital receipts before or after the payment and is sometimes required to be shown at an exit.
Pros
- Barcode-based self-checkout is Simple and cost-effective for retailers to implement.
- It works well in grocery stores, convenience stores, and retail shops because of the ease to integrate with existing POS and inventory systems.
Cons
- Requires barcode availability on all products.
- Customers may struggle with scanning certain items (e.g., loose produce).
2. QR Code-Based Self-Checkout
Another approach to implementing mobile-based self-checkout systems is to use a QR code – either during entry, or place them on product shelves. When the shopping session starts, the shoppers can scan item-specific QR codes or enter product details manually in the app. Shoppers pay through the app and leave with a digital receipt.
Pros
- QR-Based experiences can be made completely checkout-free in small retail spaces – no hassle, no delays and no rush.
Cons
- Manual QR code scanning can be slower than barcode scanning. That’s why it’s not ideal for large inventories with many products.
3. RFID-Based Self-Checkout
Retailers attach RFID tags to products. When customers place items in a designated RFID-enabled self-checkout zone, the system automatically detects all items, adds them to the app cart, and allows payment.
Pros
- RFID-based self-checkouts need no manual scanning – that’s why they are fast.
- The overall setup reduces fraud by detecting unscanned items – in time.
- RFID-based self-checkouts are ideal for fashion retail, electronics stores, and libraries.
Cons
- RFID-based checkouts are expensive to implement: the tags, readers and overall infrastructure take human effort too. (RFID tags, readers, and infrastructure).
- Not all products may be compatible with RFID.
4. AI-Powered & Camera-Based Self-Checkout
Some retail chains also use mobile apps that use AI-powered cameras to recognize items in the cart. These AI-powered cameras are even used at self-checkout stations – so customers can detect items either way.
Pros
- AI-Powered cameras eliminate the need for scanning product barcodes and using RFID tags
- It presents a highly automated and frictionless experience that is suitable for cafeterias, smart vending machines, and autonomous stores.
Cons
- Expensive to develop and maintain.
- Requires advanced AI and object recognition technology.
5. Fully Autonomous Stores (Amazon Go-Style) – Just Walk Out Technology
In stores where just-walk-out technology by Amazon is implemented, customers enter using a mobile app linked to their payment method. AI-powered cameras and sensors then track the items they pick up. Upon exit, the system automatically charges the customer without requiring manual checkout, as well a top mobile app development company in dubai can bring similar innovative solutions to businesses.
Pros
- It’s real effortless – no checkout process ideal for high-traffic areas like airports and convenience stores.
Cons
- Requires a significant investment in AI, sensors, and infrastructure.
- Serious privacy concerns due to continuous surveillance.
So, which self-checkout approach is best for your business?
As a business analyst serving clients at Techlancers Middle East for 3 years, I have witnessed that:
- small and mid-sized retailers benefit from barcode scanning or QR-based solutions as they are cost-effective and easy to implement.
- large retailers can afford RFID or AI-powered solutions so why not use it to improve efficiency and reduce fraud.
- premium stores implement Just-Walk-Out technology for the best customer experience and they have high investment.
However, what kind of self checkout software and equipment will suit your particular business highly depends on the nature of your operations, the niche, the rush hours. I would recommend sharing your business requirements with a self checkout software development company in Dubai and working out a thorough feasibility analysis before investing in the discovery or UX stage.
Build a Self-Checkout for Your Business
Share you business challenges and we’ll take it from there. Get a no-obligation FREE proposal within 24 hours and we’ll take it from there. Have the prototype? Let’s build it together!
6 Best Practices for Self-Checkout Development
Consider these 6 best practices to develop an efficient and user-friendly self-checkout system mobile app:
Optimize Camera Functions for Accurate Product Recognition
For a smooth self-checkout experience, the camera needs to work efficiently under different conditions.
- AI and computer vision help recognize products without barcodes, which is essential for fresh produce.
- Barcode and QR code scanning should be fast and accurate, even in poor lighting.
- To assist users, UI overlays, haptic feedback, and clear instructions can guide them if a scan fails. Then, multiple scanning modes, like batch scanning, speed up the process when checking out multiple items at once.
Tech Stack: OpenCV, Google ML Kit, Amazon Rekognition
Create a Responsive & Intuitive UI
A self-checkout UI should be simple and fast, with minimal steps to complete a purchase.
- Large, easy-to-tap buttons for scanning, payment, and editing improve usability.
- Real-time cart updates help users track their scanned items, while undo and edit options let them make changes before paying.
- If something goes wrong, clear error messages like “Barcode not detected – try again” should guide users.
Tech Stack: React Native, Flutter, Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android)
Incorporate Digital Payment Methods for Seamless Checkout
Offering multiple payment options like Apple Pay, Google Pay, credit cards, and digital wallets makes checkout quick and convenient.
- One-tap payments with saved cards speed things up even more.
- Features like PCI DSS compliance, tokenization, and biometric authentication (Face ID, fingerprint) protect transactions.
- For users with unstable internet, an offline payment mode can queue transactions until connectivity is restored.
Tech Stack: Stripe, PayPal SDK, Square API, Razorpay
Enhance Fraud Prevention & Security
Preventing fraud is key in self-checkouts, and AI-powered models can detect unusual behavior, such as missing scans or checkout manipulation.
- RFID or NFC verification adds an extra layer of security, especially for high-value items. R
- andomized manual checks on flagged transactions can deter theft.
- To protect sensitive data, all transactions should be encrypted end-to-end.
Tech Stack: AWS Cognito, Firebase Authentication, Azure Security
Ensure Seamless Backend Integration
A self-checkout system must sync in real-time with POS and inventory management to update stock levels instantly.
- Omnichannel integration ensures users have a consistent experience whether shopping in-store, online, or via mobile.
- An API-first approach makes it easy to integrate with third-party systems, keeping the platform scalable.
Tech Stack: GraphQL, RESTful APIs, Firebase Firestore, AWS Lambda
Improve Customer Experience & Engagement
A great self-checkout doesn’t just make payments easier—it also enhances the customer experience. For example:
- Integrating a loyalty program allows users to earn and redeem rewards automatically.
- Personalized offers based on purchase history can increase engagement.
- Accessibility features like voice commands and gesture support make checkout even more user-friendly.
- Lastly, adding real-time chat support or self-help guides helps customers resolve issues quickly.
Tech Stack: Twilio (chat support), Google Dialogflow (voice commands), Firebase Analytics (personalization)
Technology Stack for Developing Self-Checkout Software
| Frontend Development | ||
| Frameworks | React Native, Flutter, Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android) | Cross-platform or native development options |
| UI/UX | Figma, Adobe XD | Design and prototyping tools |
| Camera & Scanning | Google ML Kit, OpenCV, ZXing | Barcode/QR scanning, image processing |
| Backend Engineering | ||
| Programming Languages | Node.js, Python (Django/FastAPI), Java (Spring Boot) | Server-side logic and API development |
| Database | PostgreSQL, Firebase Firestore, MongoDB | Data storage and retrieval, real-time synchronization |
| Inventory Management | SAP, Odoo, Zoho Inventory | Integration with existing inventory systems |
| Payment Processing | ||
| Payment Gateways | Stripe, PayPal, Square, Razorpay | Online payment processing |
| NFC Payments | Apple Pay, Google Pay | Contactless payment options |
| Security & Encryption | PCI DSS Compliance, Tokenization, OAuth2, JWT Authentication | Secure transactions and user authentication |
| Automation | ||
| Computer Vision | TensorFlow, OpenCV, Amazon Rekognition | Product recognition, image analysis |
| Fraud Detection | AWS Fraud Detector, Azure AI, Google Cloud AI | Identifying and preventing fraudulent activities |
| Deployment | ||
| Cloud Providers | AWS (Lambda, S3, EC2), Google Cloud, Firebase | Cloud infrastructure for hosting and scalability |
| CI/CD | GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD | Automated build, testing, and deployment processes |
Step-by-Step Guide to Developing a Self-Checkout App for a Retail Store
Here’s a quick rundown with an insider look of how we develop customized self-checkout software at Techlancers.
Step 1: Define Business Requirements & User Flow
A business analyst connects with business stakeholders and decision-makers like you to understand the key requirements, goals, budget, design vision and so on. Then we ask them to decide if their mobile application/software will be store-specific or sync for multiple locations. Based on their answers, we recommend them options and ask them to discuss their preferences as per the budget allocations from:
- Barcode/QR scanning
- AI-based product recognition (optional)
- Real-time cart updates & modifications
- Digital payments (multiple options)
- Receipt generation & loyalty program integration
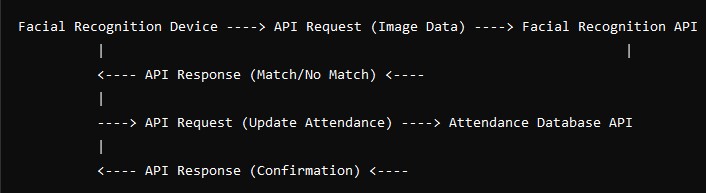
Step 2: Build the Backend & API Integration
Once designated to the design and development teams, developers start working on the client-side prototype. After this approval, the backend, which is the server-side starts with architecture.
Database developers set up a database management system to store inventory, pricing, and user transactions. Then the backend engineers develop a RESTful or GraphQL API to handle:
- Product lookup by barcode/AI
- Cart updates & pricing calculations
- Payment processing
- Inventory sync with POS
- Order & receipt generation
Step 3: Implement the Barcode & AI-Based Product Recognition
Based on the business requirements, some developers take the basic approach (use ZXing for barcode/QR code scanning), while others take the advanced approach and train an AI model with TensorFlow or OpenCV for visual product recognition (useful for grocery stores dealing in fresh produce).
Step 4: Develop the Mobile App (Frontend)
To save time and financial resources, we choose React Native (for cross-platform) development. In case businesses wat to go native, we work with Swift/Kotlin to become device-specific.
During this process, we implement scan feature, cart management, price calculation and checkout screen
Step 5: Integrate Secure Payment Processing
This step deals with all online payment-related matters. For example, we use Stripe/PayPal/Square API to handle transactions and implement tokenization & PCI DSS compliance for security.
For contactless payments, we add Apple Pay & Google Pay, and Provide bnpl (split payments into installments) or wallet balance options (if needed).
Step 6: Implement Fraud Prevention & Security
The cybersecurity developers add AI-based fraud detection to flag suspicious transactions. We also recommend using multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user login. Last step is typically implementing randomized manual checks for high-value transactions.
Step 7: Connect with Inventory & POS System
We use APIs to sync the checkout app with SAP, Odoo, Zoho Inventory, or a custom POS system and ensure real-time stock updates to avoid overselling.
Step 8: Test, Deploy & Optimize
Before this step, the major development tasks are done. So here we initiate the quality checks and fixing. Here’s how we test:
- Check scanning accuracy, payment processing, and UI responsiveness.
- Get feedback from real customers before launch.
Once all fixes are done and the app is QA-passed, we use AWS/GCP/Firebase for scalability, and use Firebase Analytics & Google Cloud Monitoring.
Over to you…
Self-checkout technology is no longer a convenience—it’s an expectation. As retailers, restaurants, and businesses continue to adopt self-service solutions, the benefits are clear – and it’s a business initiative you can afford! Whether implemented through kiosks or mobile apps, self-checkout empowers businesses to streamline operations while providing a seamless, modern shopping experience. Because the way people shop is evolving, and businesses must evolve with it, now is the time to future-proof your business with self-checkout technology.
-
Posted By – Saba Sohail
Saba Sohail is a business analyst for client-side software solutions. She has extensive expereince in mobile app development strategy, technology stack, software development cost optimization, cloud computing, product scaling and SaaS monetization.
Table of content
- What is Circle to Search?
- How Techlancers Seized This Opportunity
- Boosted Our Local SEO Efforts
- Implemented A Picture Perfect Strategy
- Made Websites More Disability-Inclusive
- Tapped into Voice Search Optimization
- Optimized Google My Business Profiles
- Combined Circle to Search with UGC

 Consulting
Consulting Development
Development Growth
Growth