Streamlining Workflows with EAM IoT and AI Automation
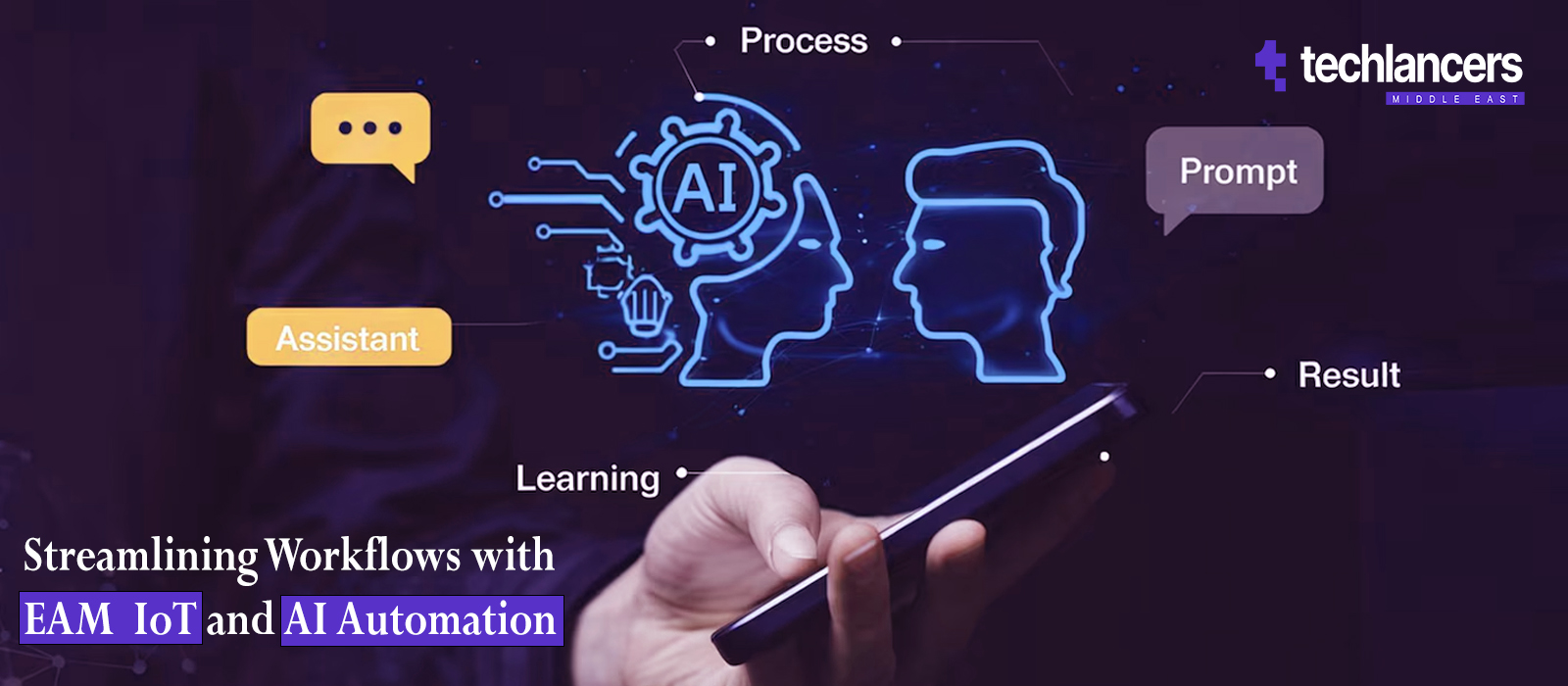
Controlling operational costs and managing asset lifecycle should be the point of focus for any business, especially enterprises with a big chunk of their capital tied up in expensive physical assets and infrastructure. Moreover, maintenance costs are always cheaper compared to the cost of asset recovery, and operational disruption. Having a robust Asset Management system on deck is key to sustainable organizational growth and operational consistency. According to Garner, CIOs must adapt to the changing dynamic of asset-intensive industries by incorporating AI, IoT, and EAM into their systems.
However, keeping real-time checks without manually inspecting machinery wasn’t possible before IoT. With AI as a new entrant, the possibilities of measuring asset lifecycle are endless and data predictions have become more accurate and understandable. A global food manufacturer has been experimenting with AI in EAM for two years, targeting everything from tractors to pumps and driving better decisions around asset throughout, utilization, and performance confirms a Sap Insider study.
In this blog post, we’ll unpack EAM and IoT and get into the details of how cloud IoT is redefining the EAM industry and helping businesses achieve their objectives.
Unpacking Enterprise Asset Management and Internet of Things
EAM stands for Enterprise Asset Management. Organizations use EAM software solutions to plan, control, schedule, and execute physical asset maintenance. With that, organizations increase asset performance and avoid any operational disruptions and unplanned machinery recovery fees.
EAM software solutions also assist in extending the life of an asset, reducing operational costs by determining the number of inventory to be ordered, and boosting environmental health and safety initiatives.
All levels of enterprise-level companies can use EAM software solutions. But mostly, EAM software has a wide acceptance and growing need in asset-intensive organizations. Enterprise-level companies utilize EAM software in one way or the other in their business to manage their asset lifecycle in different locations and departments through a single dashboard.
The global EAM market is projected to grow significantly, reaching $19.68 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.9% from 2023 onward. That’s only the tip of the iceberg. With AI and IoT working in tandem, the likelihood of breaking the market cap for EAM is high.
IoT is a transformative technology that has connected industrial machinery to our desktop computers with a click of a button. With sensors and software tailored for asset management, IoT extends digital connectivity to a wide range of physical assets. The IoT-embedded devices continuously collect data and transfer the information to cloud servers that are globally accessible for business owners maintaining the flow of critical information through the Internet.
How EAM, IoT, and AI Work Together for Optimized Asset Performance
IoT, AI, and EAM convergence is a powerhouse of data information and a hub of informed critical decision-making. Both infrastructural and software architectures, when combined offer a host of benefits for asset-intensive businesses looking to manage, maintain, and streamline their operations.
Predictive Analysis and Asset Maintainance
Predictive analysis and asset maintenance are the cornerstones of IoT and EAM fusion. The IoT sensors are capable of detecting and sharing irregularities in assets such as machinery in conjunction with EAM software solutions. The EAM’s ability to analyze IoT data is transformative allowing businesses to better understand patterns and schedule maintenance work before any operational failure. This data-driven approach to maintenance allows asset-intensive businesses to automatically schedule maintenance with either third-party vendors or the internal maintenance department. A mobile app development company in dubai can further enahnce this integration by building custom solutions.
However, the predictive analysis generated through EAM and IoT is raw. Meaning, that businesses have to make strategic decisions based on several machinery and production factors before deciding when should the scheduled maintenance occur. This causes minor or sometimes major delays in production – especially for FMCG companies that have daily work-order management.
Thanks to AI, predictive analysis has become more streamlined allowing businesses to work with a set of more structured data and planned variations for production management and asset lifecycle health. Besides refining predictive analysis, AI is also capable of learning user and machine behavior allowing businesses to optimize work through efficient asset utilizations. For instance, if an asset is incapable of working well during summer days, AI in IoT can help streamline production and machinery timings to maximize workload during cold days and cutback workload during the bustling heat, managing the overall monthly deliverables – common examples include high-capacity or industrial-grade printers.
Advanced Asset Tracking
IoT-enabled equipment has sensors that can be accessed via GPS to track asset transportation. This has a major role for logistics companies that either order industry-grade machinery or require heavy equipment to maintain their existing assets.
Asset tracking is also key to managing work schedules and timings. Business units responsible for meeting daily production targets require additional information from the logistics to make accurate production decisions. When all the information is centered on organizational level EAM, tracking assets via IoT enables production units to plan their schedule accordingly.
However, hiring human resources to plan and execute tracking-based production is redundant and limiting. AI plays a pivotal role in reducing work friction by estimating the best production times in convergence with IoT-backed data. The fusion of all three major tech and software entities allow businesses to cut operational costs, optimize human resources, and maximize asset usage efficiency.
Scalability and Adaptability
Scalability and adaptability are key features that enable EAM software systems to be flexible thanks to IoT and AI. This characteristic is crucial for any EAM system to ensure businesses grow at a smooth rate and don’t hinder production – especially for asset-intensive enterprises.
Scalability allows EAM systems to manage an increasing number of assets with minimum operational cost. IoT keeps track of all assets, equipment, and machinery keeping their lifecycle in check. On the other hand, AI assists in analyzing the need for new equipment to facilitate growing demand. AI incorporates all sales and marketing data allowing the IoT sensors to determine the maximum output capacity needed to meet the rising demand. This information is forwarded to EAM system with structured data assisting business owners in purchasing new inventory or machinery to manage their increasing market demand, Additionally web development services in dubai can integrate dashboards and platforms for real-time data.
Adaptability allows EAM systems to quickly integrate new assets and their performance metrics with little to no third-party interaction. In addition, AI with EAM allows businesses to automatically place orders for depleting inventory while managing the vendor’s supply time and demand in balance.
Ending Note
The convergence of EAM, IoT, and AI is transforming asset management by streamlining operations, enhancing predictive maintenance, and optimizing asset performance. With these technologies working in harmony, businesses can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and make smarter, data-driven decisions. As the industry continues to evolve, integrating these advanced tools will be key to staying competitive and achieving sustainable growth in asset-intensive environments.

-
Qasim Ali
Senior Brand Manager/Editor
With 7 years of experience in the Content and SEO industry, I lead a team of writers and SEO specialists turning traffic to conversion making all content linkable and rank able.

 Consulting
Consulting Development
Development Growth
Growth


